[LeetCode][python3]0015. 3Sum
Start the Journey
N2I -2020.03.21
1. My first try
class Solution:
def threeSum(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
ans=[]
nums.sort()
#print(nums)
for i in range(len(nums)-2):
if nums[i]>0:
break
if i==0 or nums[i]>nums[i-1]:
j=i+1
k=len(nums)-1
while j<k:
if nums[i]+nums[j]+nums[k] == 0:
ans.append([nums[i],nums[j],nums[k]])
j+=1
k-=1
while j<k and nums[j]==nums[j-1]:
j+=1
while j<k and nums[k]==nums[k+1]:
k-=1
elif -nums[i]>nums[j]+nums[k]:
j+=1
else:
k-=1
#print(ans)
return ans
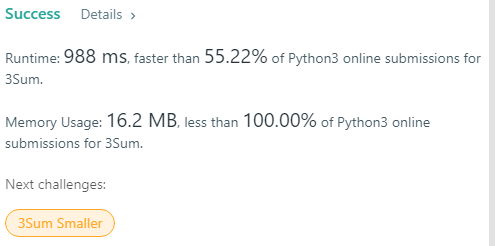

Explanation:
The classic way to solve this problem. The range between 700 ms to 1100 ms are probably the same method. First you sort the array, then search the array with three pointers.
2. A Recursive Solution
class Solution:
def threeSum(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
if not nums:
return []
nums = sorted(nums)
res = []
self.kSum(nums, 0, len(nums)-1, 3, 0, [], res)
return res
def kSum(self, nums, left, right, k, target, state, res):
# if the selecting range is not enough
if k < 2 or right - left + 1 < k:
return
if k * nums[left] > target or k * nums[right] < target:
return
if k == 2:
# Solving 2Sum problem
while left < right:
cur = nums[left] + nums[right]
if cur == target:
res.append(state + [nums[left], nums[right]])
left += 1
while left < right and nums[left] == nums[left - 1]:
left += 1
elif cur > target:
right -= 1
else:
left += 1
else:
# k > 2, reduce the degree
for i in range(left, right+1):
if i == left or i > left and nums[i] != nums[i-1]:
self.kSum(nums, i+1, right, k-1, target-nums[i], state+[nums[i]], res)
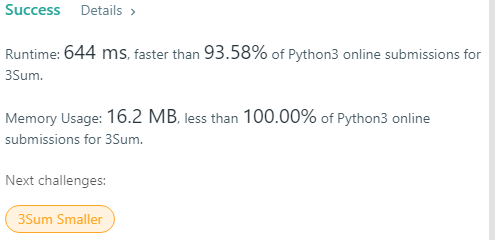
Explanation:
The solution is a classic recursive way to solve this kind of problems. It reduce its degree in every recursion. Puts any situation into a 2 Sum problem.
3. A Better Solution
class Solution:
def threeSum(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
ans = set()
count = {}
for i in nums:
if i not in count: count[i] = 1
else: count[i] += 1
nums = sorted(count)
for i, item_i in enumerate(nums):
if item_i < 0:
target = -item_i
left = bisect.bisect_left(nums, target - nums[-1], i + 1)
for item_j in nums[left:bisect.bisect_right(nums, target // 2, left)]:
item_k = target - item_j
if item_k in count and item_k != item_j:
ans.add((item_i, item_j, item_k))
if count[item_i] > 1:
if item_i == 0:
if count[0] > 2:
ans.add((0, 0, 0))
else:
if -2 * item_i in count:
ans.add((item_i, item_i, -2 * item_i))
return ans

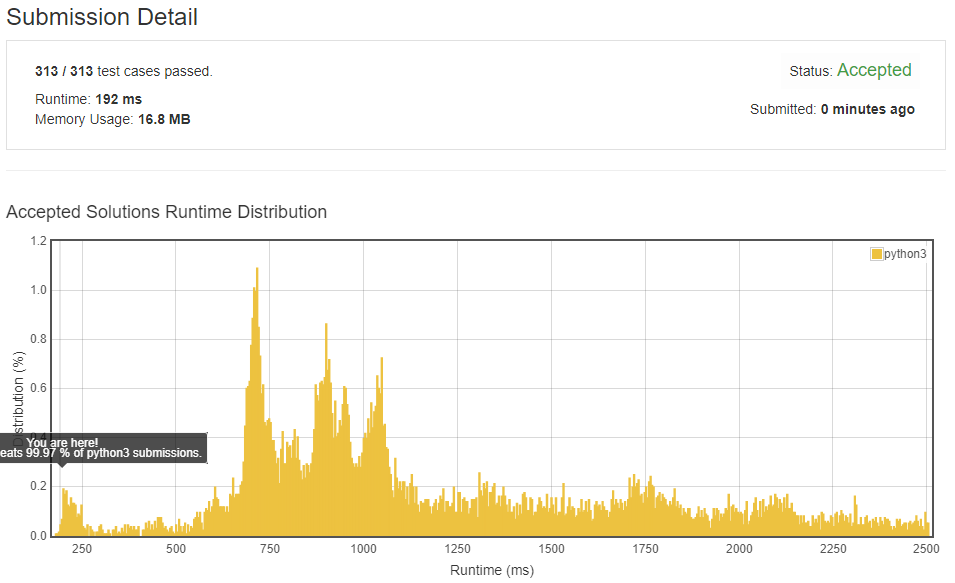
Note:
bisect.bisect_left(a,x,lo=0,hi=len(a))A function using binary search to find the target valuexand return the index of it. If there are multiplex, return the first index. If there are none, return the indexxshould be insert in and remain the array sorted.ais the searching array.xis the target.loandhiis the searching area ofa.
print("example of bisect_left")
import bisect
a=[0,1,2,3,3,4,6,7]
x=4;print(bisect.bisect_left(a,x))
#>>5
x=3;print(bisect.bisect_left(a,x))
#>>3
x=5;print(bisect.bisect_left(a,x))
#>>6
x=5;print(bisect.bisect_left(a,x,2,4))
#>>4
Explanation:
The solution is probably the fastest solution among the solutions in Leetcode. It is a close methon to the first solution above, but it reduce the searching area to
(target+nums[-1],target//2), that reduces time spent in every for loop.
Comments
Post a Comment