[LeetCode][python3]0018. 4Sum
Start the journey
N2I -2020.04.02
1. My first try
class Solution:
def fourSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[List[int]]:
ans=[]
nums=sorted(nums)
for a,tar_a in enumerate(nums[:-3]):
b=a+1
for tar_b in nums[a+1:-2]:
c=b+1
d=len(nums)-1
while d>c:
#print(a,b,c,d)
tar_c=nums[c]
tar_d=nums[d]
if tar_a+tar_b+tar_c+tar_d==target:
if [tar_a,tar_b,tar_c,tar_d] not in ans:
ans.append([tar_a,tar_b,tar_c,tar_d])
else:
c+=1
d-=1
elif tar_a+tar_b+tar_c+tar_d>target:
d-=1
else:
c+=1
b+=1
return ans
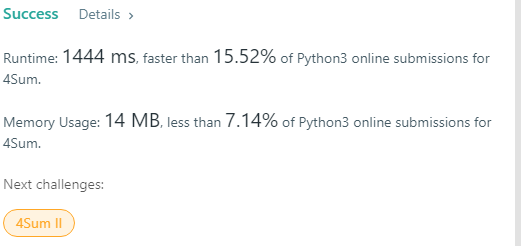
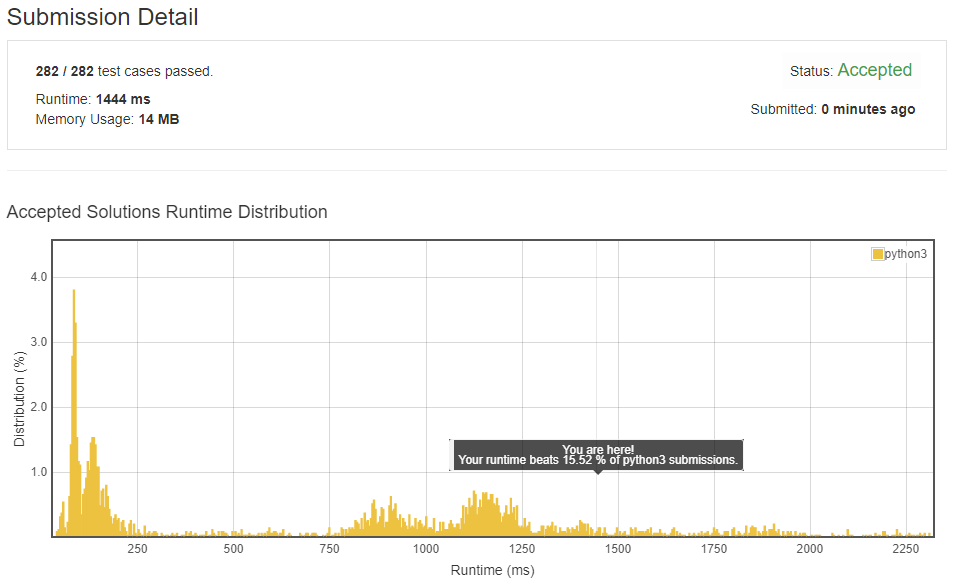
Explanation:
This is a classic way to solve 4 sum problems. It is better than an O(n³) solution but still cost too much time.
2. A Recursive Solution
class Solution:
def fourSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[List[int]]:
if not nums:
return []
nums = sorted(nums)
res = []
self.kSum(nums, 0, len(nums)-1, 4, target, [], res)
return res
def kSum(self, nums, left, right, k, target, state, res):
# not enough
if k < 2 or right - left + 1 < k:
return
if k * nums[left] > target or k * nums[right] < target:
return
if k == 2:
# reduce to 2 sum problem
while left < right:
cur = nums[left] + nums[right]
if cur == target:
res.append(state + [nums[left], nums[right]])
left += 1
while left < right and nums[left] == nums[left - 1]:
left += 1
elif cur > target:
right -= 1
else:
left += 1
else:
# k > 2, reduce the degree
for i in range(left, right+1):
if i == left or i > left and nums[i] != nums[i-1]:
self.kSum(nums, i+1, right, k-1, target-nums[i], state+[nums[i]], res)

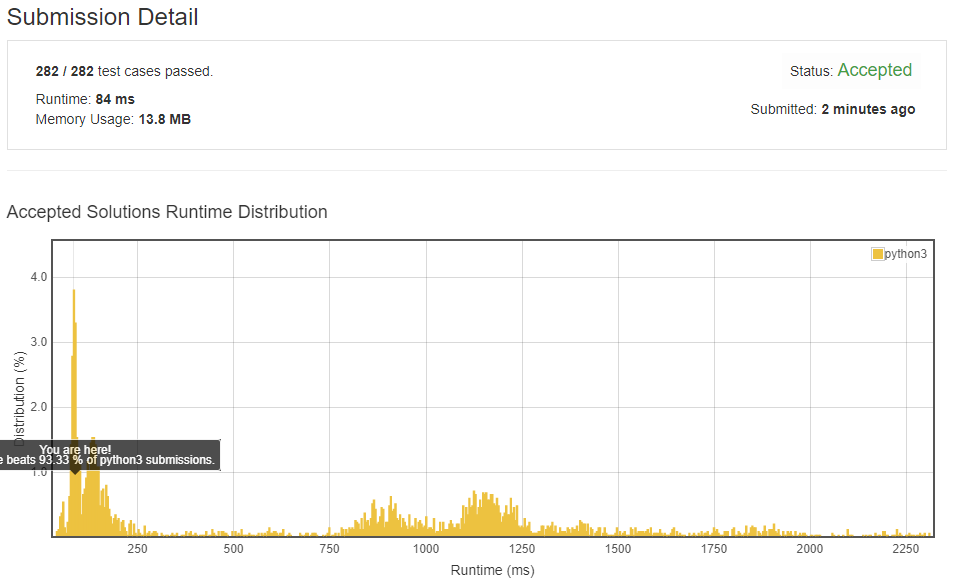
Explanation:
The solution is a classic recursive way to solve this kind of problems. It reduce its degree in every recursion. Puts any situation into a 2 Sum problem.
3. A better solution
class Solution:
def fourSum(self, nums, target):
if not nums:
return []
nums=sorted(nums)
numsLen = len(nums)
dic = {j:i for i, j in enumerate(nums)}
ans = set()
N = nums[-1]
for idx, num1 in enumerate(nums[:-3]):
if num1 + 3 * N < target:
continue
if 4 * num1 > target:
break
for j in range(idx + 1, numsLen - 2):
num2 = nums[j]
if num1 + num2 + 2 * N < target:
continue
if num1 + 3 * num2 > target:
break
for k in range(j + 1, numsLen - 1):
c = nums[k]
temp = target - num1 - num2 - c
if temp > N:
continue
if temp < c:
break
if temp in dic and dic[temp] > k:
ans.add((num1, num2, c, temp))
return ans

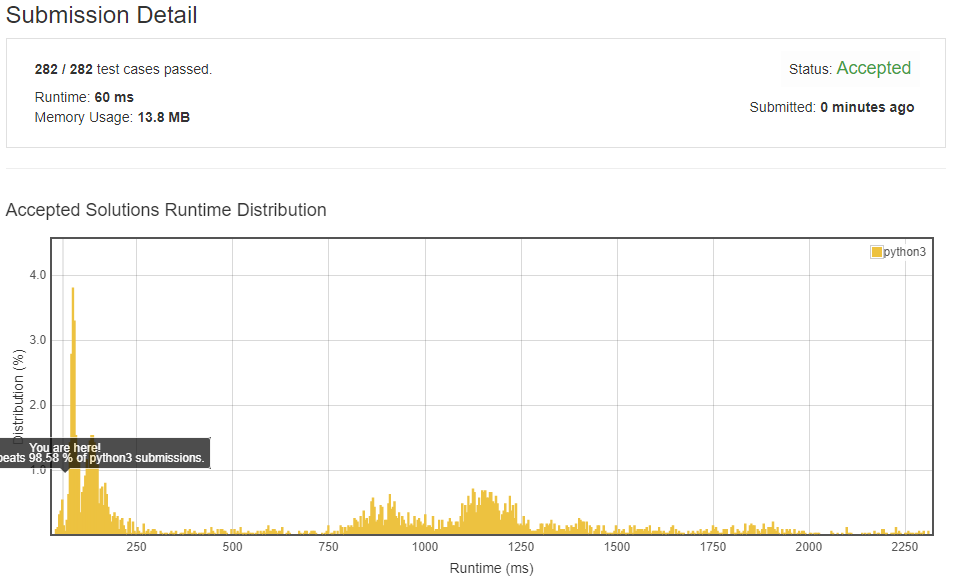
Explanation:
The main idea in the solution is to limit the searching fragment and low down the time cost. The two
if condition num1+num2+2*N<target and num1+3*num2>target are the keys. They are both conditions with results no answers in all kind of situations. The dic saves the last index of every duplicate numbers. The solution use this to check if answer is unique.
Comments
Post a Comment